
|
Learn more about Toad for SQL Server Find solutions and downloads at the |

|
Learn more about Toad for SQL Server Find solutions and downloads at the |
| < To bookmark a page, right-click the Page Title and select Add to Favorites / Bookmark This Page |
Toad for SQL Server 5.7 |
The Query Builder enables you to create a query without writing or editing SQL statements. Even if you are familiar with SQL, the graphical interface makes it easier to create relationships and visualize the query.
To build a query
Click ![]() (ALT+T+Q).
(ALT+T+Q).
Drag tables and views from the Object Explorer to the Diagram pane.
Join columns by selecting a column in a table and dragging it to a column in another table. A connector line displays between the two objects to visually represent the relationship.
Note:
By default, all joins are initially created as Inner
Joins. Double-click ![]() to modify the join type. See Join Columns for more information.
to modify the join type. See Join Columns for more information.
Add columns to the query using one of the following methods:
Select each column you want to add to the query.
To add all columns to the query using a SELECT * statement, select * (Wildcard) . If selected, an asterisk displays for the Field name in the Criteria tab.
The selected columns display in the Criteria pane in the bottom portion of the Query Diagram window (see the following image).
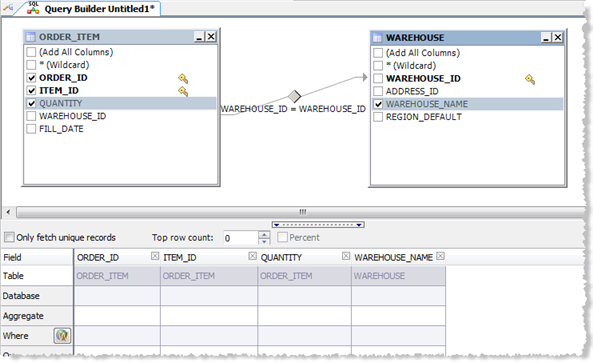
Notes:
Select
the type of statement you want to create (default is Select
Statement):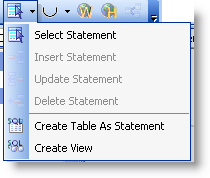
Notes:
Use the Criteria pane (bottom portion of the Query Diagram window) to specify the query options. Review the following for additional information:
|
Only fetch unique records |
Select this checkbox to eliminate duplicate records from query results. |
| Top row count |
Enter the number of records that you want to return that have the highest values. You can also select the Percent checkbox to select a percentage of records to return instead of an exact value. |
|
Aggregate Function |
Select one of the following functions to calculate column values:
Note: If you add a Group By clause, you must specify an aggregate function for any remaining columns. |
|
Where Condition |
Use to compose a Where clause or to add a subquery.
Notes:
|
|
Or |
Select the operators and expressions to add to the OR condition. See Add Or Conditions for more information. |
|
Group By |
Select the column you want to add the Group By clause to and click +. You can add a new Group By clause to any remaining columns to group them in sequence. Any remaining columns that do not have a Group By clause must include an aggregate function. Tip: You can add a Group By clause to all selected columns in each table/view, by right-clicking the Diagram pane and selecting Add Group By. |
|
Having Condition |
Select the operators, aggregate, and expressions to include in the Having condition. This option is disabled unless you have set a Group By clause. See Set Having Conditions for more information.
Note: If you reverse engineer a query that contains a Having condition from the Editor or edit it in the Query tab of the Query Builder, it displays in a Global Having clause bubble (click here to see an example) on the Diagram pane rather than the Having Condition field below the Diagram pane. You can double-click the Global Having clause to edit it. |
|
Sort |
Select an option to add this column to the Order By clause and specify a sort direction. |
|
Visible |
Select this checkbox to return this column in query results. This is useful if you need to include a column in the selection criteria, but do not need to display it in the query results. |
|
Field Alias |
Enter a name to use as an alias for the column name in the query results. This is useful if you have an ID or vague column name and want to easily identify that column in the query results. |
|
Table Alias |
Enter a name to use as an alias for the table name in the query results. For example, if there are multiple employee tables that you need to join for the query, you can rename the tables to permanent, contract, etc., to easily identify them. Note: If you selected All Columns for a table or created a column using the Edit Calculated Fields window, you cannot modify the table alias. |
Add a subquery, if needed. See Add Subqueries for more information.
Click ![]() to execute the query.
to execute the query.
To save the query, right-click
the Query Builder tab and select Save
File. If you save the file as a Query Builder file (.tsm), Toad
saves the current connection with the file and you cannot change it by
switching connections. To view the connection associated with the file
and preview the script, place the cursor over the Query Builder tab (see the following image).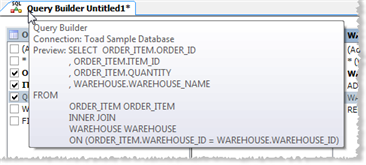
You can also save a query and any results sets in a Toad editor
file (.tef). This file format is useful for building scripts that have
large result sets that you do not want to continue executing or for saving
results when you have not finished building a script.
Tips:
When opening a previously saved Query Builder file, you can right-click the Diagram pane and select Refresh to get the latest objects from the database, including added/removed columns and data type updates.
An * in the title of the object indicates that the saved version differs from the database version.
To view details for a table
in the Diagram, click ![]() (SHIFT+F4). If a table is not selected, details
for the last selected table display.
(SHIFT+F4). If a table is not selected, details
for the last selected table display.
To create a data report, pivot grid, or chart from the data, right-click the data and select Send To | report_type.